Converting materials into finished products takes a lot of energy, especially when it’s footwear. Nike’s Sustainable Manufacturing & Sourcing (SM&S) Energy & Carbon Program works with contract manufacturers through coaching and consulting to reduce energy use and carbon emissions at manufacturing facilities. The program drives carbon reduction through resource productivity and renewable energy.
Nike approaches efficiency through the Nike Energy Minimum Program, an energy management foundation geared at achieving energy and cost savings. This program brings organizational capabilities, data analytics and energy management activities to its contract manufacturers. Additionally, Nike work with individual facilities to scale key energy efficiency opportunities that will have the greatest impact on their unique energy and carbon footprint.
Once the Energy Minimum Program is implemented at its factory partner’s facilities, Nike gains valuable knowledge of energy management and performance. Nike reviews the information on a monthly basis to help develop baselines, targets, and other useful analytics to tailor the program’s approach to each individual factory. Performance is reviewed back with factories every quarter so they can plan future projects for improvement.
Since launching this effort in 2008, Nike footwear suppliers that account for more than 80 percent of volume have collectively reduced their energy use by 55 percent. That means, today it takes less than half the energy to make a pair of shoes than it did ten years ago. The program is active in 5 regions including Greater China, South Asia, South East Asia, EMEA, and Americas and in more than 15 countries across Nike’s contracted manufacturing supply chain.
In China, the Energy & Carbon Program has focused on driving energy management through different projects by eliminating inefficient equipment and retrofitting outdated components with more efficient ones. Initiatives in the Energy & Carbon program include the elimination of centralized steam boiler systems and implementing new and more efficient electric motors through a management system. More specifically, Nike promotes the use of IE3 electric motor retro-fits for all large motors, and in inventory for all future motor replacement. In 2017, nine of Nike’s strategic suppliers in China that make up close to 10 percent of Nike footwear manufacturing volume eliminated the use of steam for production of footwear.
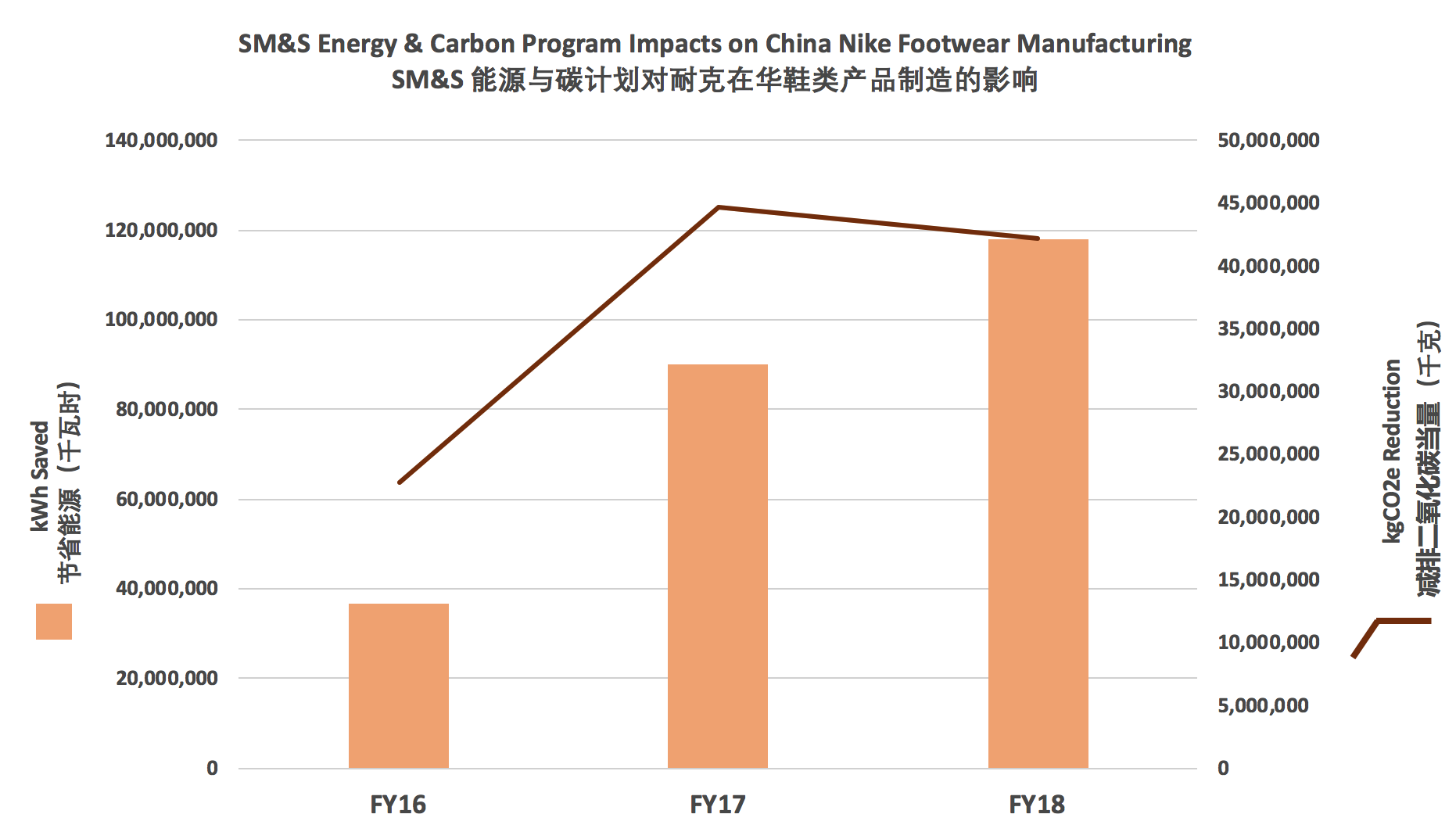
From FY15 to FY18, total Nike strategic footwear suppliers in China have reduced the energy to produce a pair of shoe by 19%. The cumulative effects of these initiatives have already saved over 117,800 MWh for all China factories. This equates to a reduction of 42,000 metric tones of CO2e.
As the SM&S Energy & Carbon Program continues to mature and our contract manufacturers become more energy efficient, our focus is shifting to drive broader adoption of renewable energy with an initial focus on solar photovoltaic (solar PV). Currently in China solar PV makes up less than one percent of strategic supplier’s energy. Nike estimates that its solar PV initiative could provide up to 20 percent of the electricity use of factory operations once implemented. It is also convening supplier working groups to accelerate manufacturing factories’ adoption of renewable energy in multiple countries including China, Vietnam, and Indonesia. At scale, this approach will eventually allow Nike’s manufacturing factories to use renewable energy to power their operations.
One of the first Nike strategic factories to implement the Energy Minimum Program in China has made significant progress in reducing energy consumption since FY15. “Factory A” was guided by Nike’s Energy & Carbon Program field team to implemente a variety of energy conservation measures:
-
in FY15, it implemented motor upgrades as well as insulation of vulcanization tanks resulting in 1,600 MWh saved annually;
-
in FY16, the factory added heat recovery and optimized its compressed air system through compressed air leak elimination, resulting in 60 MWh saved annually;
-
in FY17, it completely eliminated steam use with decomishining of boilers achieving 10,500 MWh saved annually.
Now with the focus on renewable energy, the factory is finalizing the installation of a 4.6 MW solar PV system that will provide close to 8 percent of total energy needs. Overall, with the implementation of the Energy Minimum Program and recommended energy conservation measures, Factory A has reduced its energy intensity (kWh/pair) by 25 percent since FY15 and reduced emissions by 10,177 metric tones of CO2e.
(The above content was provided to IPE by the brand, who is responsible for the accuracy of the data. This document is bilingual. If any questions arise related to the accuracy of the information
contained in this translation, please refer to the English version
of the document, which is the official version of the document.)